Computer Science (New) - For Class IX - UNIT. 4. Data Communication And Computer Network - Short and Descriptive Questions Answers
Computer Science (New) - For Class IX - UNIT. 4. Data Communication And Computer Network - Short and Descriptive Questions Answers
GO TO INDEX
Chapter No.4. Data Communication And Computer Network
Descriptive Questions Answers
Q.1: Define communication and data communication?
Ans: COMMUNICATION:
Communication is the process of sharing a message.
Example:
A conversation between two people is an example of communication.
DATA COMMUNICATION:
Data communications refers to the sharing of a virtual message. Data communication is the exchange of digital messages between two devices. It involves a sender and a receiver which communicate via some form of transmission medium such as a cable.
Example:
Electronic communications, like emails and instant messages and phone calls are examples of data communications.
Q.2: Define the following terminologies of data communication?
- Data
- Data Communication
- Data Transmission
- Analog Signals
- Digital Signals
- Data Rate / Bit Rate
- Baud Rate
- Signal to Noise Ratio
Ans: BASICS TERMINOLOGIES OF DATA COMMUNICATION
(i) Data:
- Collection of raw facts and figures is called data. The word data is derived from Latin language and it is plural of Datum.
- The text, numbers, symbols, images, voice and video which are processed by computers and digital devices are called data. Data can be considered as unprocessed information.
(ii) Data Communication:
Data Communication is the process of transferring data electrically from one place to another. It is the process of exchange of data and information between two partiesExample: Such as human and electronic or computing device.
(iii) Data Transmission:
The data transmission means emission of data in any direction via wireless or wired medium. Transmission may occur between source and destination.
(iv) Analog Signals:
Analog signals are a continuously varying signals or waves that change with time period and used to represent data. An analog signal can be used to measure changes in some physical quantities
Example: Such as light, sound, pressure or temperature.
(v) Digital Signals:
A digital signal is an electrical signal that is converted into a pattern of bits to represent a sequence of discrete values, at any given time. It can only be one of the finite numbers represented as 0 or 1.
(vi) Data Rate / Bit Rate:
- Data rate is the rate at which data is transferred. It is normally measured in bits per second. Bit is the actual binary digit which is the basic unit of data transmission. Bit can hold either 0 or 1.
- Bit Rate:
Data rate can be ranging from bps (bits per second) for smaller values to kbps (kilo bits per second) and mbps (megabits per second). It is also called bit rate. - Data rate becomes faster when more bits are transferred in one second.
- Formula Of Bit Rate:Bit rate = baud rate x the number of bits per signal units.
(vii) Baud Rate:
- The baud rate is the number of signals transmitted per second and one signal can represent one or more bits. It is used to describe the maximum change in an electronic signal.
- For example, if a signal changes 1200 times in one second, it would be measured at 1200 baud.
- Formula of Baud Rate:Baud rate = bite rate / the number of bits per signal units.
(viii) Signal to Noise Ratio:
- Signal-to-noise ratio (abbreviated SNR or S/N) is a measure. It is dened as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels.
- Uses: It is used in engineering that compares the level of a desired signal and the level of background noise.
Q.3: Differentiate between:
(a) analog and digital signals
(b) Data rate or Bite rate and baud rate?
Ans: Difference Between Analog Signals and Digital signals
| S.No. | Analog Signals | Digital signals |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | An analog signal is a continuous wave that changes by time period. | A digital signal is a discrete wave that carries information in binary form. |
| 2. | Analog signal has no fixed range. | Digital signal has a finite number i.e. 0 and 1. |
| 3. | An analog signal can easily be disturbed by other signals or waves. | A digital signal is less prone to other signals disturbance. |
| 4. | The human voice is example of an analog signal. | Signals used by computer are the digital signal. |
| 5. | An analog signal is represented by a sine wave. | A digital signal is represented by square waves. |
| 6. | Analog signals are long term waves need to be boosting. | Digital signals are short term signals remain within digital devices / electronic. |
Difference between Data Rate/Bit Rate and Baud Rate:
| S.NO. | Data Rate/Bit Rate | Baud Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bit rate tells the number of bits transmitted per unit of time (Second). | Baud rate is used when we want to know the number of signal units transmitted per unit of time (Second). |
| 2. | Bit rate is the number bits (0's and 1's) transmitted per second. | Baud rate is the number of times a signal is traveling comprised of bits. One signal can represent more than one bit. |
| 3. | Formula: Bit rate = baud rate x the number of bits per signal unit | Formula: Baud rate = bit rate / the number of bits per signal unit |
Q.No.4: Explain different components of a communication system using examples? Also write down single example?
Ans: COMPONENTS OF A COMMUNICATION SYSTEM:
A Communication system has following ve components:
(i) Message:
It is the information or data to be communicated.
Example: Common forms of information include text, numbers, pictures, audio and video.
(ii) Sender:
It is the device that generates and sends a message.
Example: It can be a computer, telephone handset, etc.
(iii) Receiver:
Any particular digital electronic device which has capability to recieve data in form of message. The location of receiving computer is generally different from the sending computer.
Example: Like sender, it can also be a computer, telephone handset, etc.
(iv) Medium:
It is the channel or path through which the message is carried from sender to the receiver.
Example: Some examples include twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, radio waves, etc.
(v) Protocol:
Protocols are the rules and procedures on which computers exchange data on network.
Sender and receiver follow same protocols to communicate with each other.
In other words, a protocol is an agreement between two parties or venders, using communication devices.
Example: FTP, TCP/IP, HTTP etc.
EXAMPLE OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEM:
When a person talk with another person directly, then the speaker is the sender who conveying the message as information in the form of sound waves through a communication channel, the intervening air and listener are the receiver.
If the distance between the speaker and the listener is large sound waves cannot reach from the speaker to the listener directly and communication is not possible. To make communication possible, different communication channel or method is used like microphone and speakers via telephone or internet services etc.
Q.5: What are the properties of a Good Communication System?
Ans: Properties of a Good Communication System:
The effectiveness of a data communications system depends on the fundamental characteristics which include delivery, accuracy and timeliness.
| S.No. | Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Delivery | Making sure that the data is delivered is the first fundamental characteristic of any communication network. The system must be able to deliver data in correct order to the correct destination. |
| 2. | Accuracy | The system must deliver the data accurately. Data that has been altered during transmission and left uncorrected is not useful. |
| 3. | Timeliness | The data must be delivered in a timely manner. Late delivered data is useless. |
Q.No.6: Define the transmission medium or communication channel. Name its group?
Ans: TRANSMISSION MEDIUM:
Transmission Medium or Communication Channel is a wireless or physical path between the sender and receiver through which data is sent and received from one place to another. Data is transmitted normally by electromagnetic or electrical signals through different types of wires, atmosphere or vacuum.
Transmission media is broadly classified into two groups:
- Guided: It has three common types, which are:
i. Coaxial
ii. Fiber Optics
iii. Twisted (a) Unshielded (b) Sheilded - Unguided: It has three major types
i. Radiowaves
ii. Microwaves
iii. Infrared
Q No.7: Define guided media and describe different types of guided media?
Ans: GUIDED MEDIA:
In guided media signals are transmitted in a narrow pathway by using physical links. It is also called Wired or Bounded transmission media. The physical links are the cables that are tangible or have physical existence.
TYPES OF GUIDED MEDIA:
There are three common types of guided media used for the networks. Each of them has its own characteristics like transmission speed, effect of noise, physical appearance, cost, etc.
- Twisted Pair Cable
- Coaxial Cable
- Fiber-Optic Cable
(i) Twisted Pair Cable:
This cable is made by two separate wires twisted together. A twisted pair cable is made up of insulated copper wires. The insulation and twisting of wires prevent external interference. Each pair of wires has unique color code.
Use: This type of cable is widely used in different kinds of data and voice infrastructures.
Types Of Twisted Pair Cable:
There are two types of twisted pair cables:
- (a) Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
- (b) Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
(a) Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP):
This type of cable can block interference but it is vulnerable to external interference. It is less expensive and easy to install.
Use: It is mostly used for telephonic applications.
(b) Shielded Twisted Pair (STP):
This type of cable consists of a special coating to block external interference.
Use: It is used in fast-data-rate Ethernet and also in voice and data channels of telephone lines.
(ii) Coaxial Cable:
Coaxial cable is also known as coax. It has an outer plastic covering containing two parallel conductors each having a separate insulated protection cover.
Use: Cable TVs and analog television networks widely use coaxial cables.
(iii) Fiber-Optic Cable:
In optical fiber or fiber-optic cable data is transferred in the form of light. It uses the concept of reflection of light through a core made up of glass or plastic. The core is surrounded by a less dense glass or plastic covering called the cladding.
Use: It is used for transmission of large volumes of data at very high speed.
Q No.8: Define unguided media and describe different types of unguided media?
Ans: UNGUIDED MEDIA:
Unguided media is also termed as wireless or unbounded transmission media. It does not require physical medium such as wire for the transmission of electromagnetic signals.
TYPES OF UNGUIDED MEDIA:
There are three major types of Unguided Media.
- Radio Waves
- Microwaves
- Infrared
(i) Radio Waves:
Radio waves are also called electromagnetic waves. These are easy to generate and can penetrate through buildings. Radio waves are omnidirectional and propagated in all directions. It means that sending and receiving antennas do not need to be aligned.
Use: FM, AM radios, television and cordless phones use radio waves for transmission.
(ii) Microwaves:
Microwave transmission is a line of sight transmission i.e. the sending and receiving antennas need to be properly aligned with each other. The distance covered by the signal is directly proportional to the height of the antenna.
Use: These are mostly used for mobile phone communications tower and television broadcast.
Types Of Microwaves:
There are two types of microwave transmissions:
(a) Terrestrial and
(b) Satellite
- (a) Terrestrial: Terrestrial microwaves have both stations having antennas on earth.
- (b) Satellite: In satellite system, some antenna are on satellite in orbit and others are on stations on earth. They work at remote places.
Use: It can be used in mobile devices.
(iii) Infrared:
It uses infrared light to transmit signals. LED is used to transmit signals and light-receivers (photodiodes) to receive signals. They use terahertz frequency. It cannot penetrate walls or other objects. Infrared light is transmitted generally line of sight (point to point).
Use: Wireless infrared communications can be used to establish short range wireless links or wireless Local Area Network.
Q.No.9: Differentiate between:
- Guided and unguided media
- Radio wave, microwave and infrared wave
Ans: DIFFERENCE BETWEEN GUIDED AND UNGUIDED MEDIA:
| S.NO. | GUIDED MEDIA | UNGUIDD MEDIA |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | In guided media signals are transmitted in a narrow pathway by using physical links. | It does not require physical medium such as wire for the transmission of electromagnetic signals. |
| 2. | It is also called Wired or Bounded transmission media. | Unguided media is also termed as wireless or unbounded transmission media. |
| 3. | Wired transmission | Wireless transmission |
| 4. | It provides direction to signal for travelling. | It does not provide any direction. Unguided media is generally suited for radio broadcasting in all directions. |
| 5. | Transmission speed is generally faster. | Transmission speed is generally slow. |
| 6. | Types: Twisted pair cable, coaxial cable and fibre optic cable. | Types: Radio wave, microwave and infrared. |
Difference Between Radio Wave, Microwave And Infrared Wave
| S.NO. | Basis | Radio waves | Microwaves | Infrared waves |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Direction | These are omni directional in nature. | These are unidirectional in nature. | These are unidirectional in nature. |
| 2. | Penetration | At low frequency, they can penetrate through solid objects and walls but at high frequency they bounce off the obstacle. | At low frequency, they can penetrate through solid objects and walls but at high they cannot penetrate. | They can not penetrate through any solid objects and walls |
| 3. | Frequency range | 3 KHz to 1 GHz | 1 GHz to 300 GHz | 300 GHz to 400 GHz |
| 4. | Security | These offer poor security. | These offer medium security. | These offer high security. |
| 5. | Attenuation | High | Variable | Low |
| 6. | Government License | Some frequencies in the radio waves require government license to use these. | Some frequencies in the microwaves require government license to use these. | There is no need of government license to use these waves. |
| 7. | Usage cost | Setup and usage cost is moderate. | Setup and usage cost is high. | Usage cost is very less. |
| 8. | Communication | These are used in long distance communication. | These are used in long distance communication. | These are not used in long distance communication. |
Q.No.10: Describe the different types of flaws and faults (impairment) in transmission signals?
Ans: TRANSMISSION IMPAIRMENTS OR FLAWS AND FAULTS IN TRANSMISSION SIGNALS:
Sometimes, signals traveling through transmission media lose their quality. This means that received signal is not same as the signal that was sent. This phenomenon is called transmission impairments. Transmission impairments are those defects that occur when data is transmitted.
CAUSES OF IMPAIRMENTS OR TYPES OF FLAWS AND FAULTS IN TRANSMISSION SIGNALS:
There are three causes of impairment i.e.:
- Attenuation
- Distortion and
- Noise
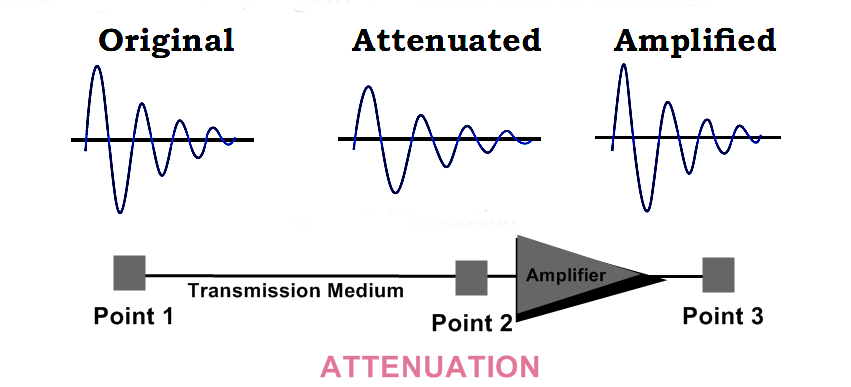
(i) Attenuation:
Attenuation means loss of energy. A signal loses its energy due to the resistance of medium while it is transmitted. Its strength decreases with increase in distance. Amplifiers are used to overcome attenuation and make signal stronger again. It is measured in decibels.
(ii) Distortion:
Distortion means change in the shape of the signal. A composite signal has several frequencies. When it travels through a medium different component of signal may reach at different time at destination because each component has different speed in that medium. This is called distortion. They have different phases at sender and receiver ends.
(iii) Noise:
Unwanted signal that mixes up with the original signal during the transmission of data is called noise. It can be induced noise, crosstalk noise, thermal noise and impulse noise which may damage the signal.
Q.No.11: Describe the communication device and their functions?
Ans: COMMUNICATION DEVICES:
Ans: A communication device is any type of hardware capable of transmitting and receiving data, instructions and information.
(i) Switch:
A switch or network switch is a networking device.
Function:
- It connects computers and other devices like printers, scanners and cameras on a network.
- Data cables from all computers and other devices of network are plugged into the switch to enable communication between them.
(ii) Router:
Routers are a combination of hardware and software.
Function:
- A Router is a device that connects two or more networks.
- The main function of a router is to determine the optimal data path and transfer the information through that path, also known as network traffic controller.
(iii) Modem:
Modem is short for Modulator and Demodulator. Modulation is the process of converting digital signals into analog signals. Demodulation is quite opposite; it converts analog signals into digital signals.
Function:
- Modem has the ability of sending and receiving signals that allows computers to share information with each other.
- This sharing of information is possible over phone lines, cables or satellite connections.
Types Of Modem:
- Dial-up Modem:
A dialup modem can be internal or external.
Function:
Dialup modems use standard telephone lines to transmit and receive information.
It is important to remember that telephone lines carry only analog signals, whereas data packets sent by the computer are in digital form. In order to send these packets across a telephone line, modem converts digital signals into analog. - DSL Modem:
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line.
Function:
Like dial-up modem DSL modem also uses telephone lines to transfer digital signals.
DSL modem has a built-in network switch which enables use of twisted pair wires to deliver data and voice at high speed as compare to dial-up modem.
Some DSL modems also have wireless communication functionality. - ISDN Modem:
Integrated Services Digital Network is a digital phone connection. It is faster and expensive technology.
Function:
It can transmit data, voice and video over a normal telephone line at the same time which was not done before.
Since ISDN work on digital transmission it converts analog voice to digital signals before transmission.
(iv) Network Interface Card (NIC):
Network cards also known as Network Interface Cards (NICs) are hardware devices. They are installed on the mother board. Modern motherboards have built-in NICs.
Function:
- It connect a computer with the network.
- They are responsible for establishing a physical connection between the network and the computer.
- Computer data is translated into electrical signals and sent to the network via Network Interface Cards.
Q.No.12: Define the term computer network? Or Define and explain the term computer network?
Ans: COMPUTER NETWORKS:
Computer networks are just like a highway on which data can travel. A computer network connects parts of distributed system including hardware and software. It shares common functions and features like data and devices which is very important nowadays.
A computer network is a group of computers and related equipment connected by a communication links to share data and other resources.
The Related Equipment may be printer, scanners, fax machines, server, etc.
The Resources may include a file server, internet connection, etc.
Q.No.13: Define the term computer networking or networking?
Ans: Networking:
Networking is the act of joining computers and its accessories so that exchange of information and sharing of resources take place.
In today's world, networking plays a vital role in computers and telecommunication fields. Modern organizations create a networking environment and device connectivity for fast, inexpensive and reliable communication.
Q.No.14: Classify the network types on the basis of their characteristics? Or Describe the types of computer networks?
Ans: Types of Computer Networks:
Computer networks can be categorized by their size as well as their purpose.
The size of a network can be expressed by the geographical area they occupy and the number of computers that are part of the network. Networks can cover anything from a handful of devices within a single room to millions of devices spread across the entire globe.
There are three types of computer networks:
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
(i) Local Area Network (LAN):
LAN is a group of computer and peripheral devices which are connected in a limited area such as school, laboratory, home and office building.
Purpose:
- Useful resources like internet access, storage space and printers can be shared through LAN.
- It can be built with inexpensive hardware such as hubs, switches, network adapters and network cables.
- Data and software are also shared through LAN.
Some examples of LAN are:
- Networking between two computers.
- Networking in the home, school, library, laboratory, college / university campus or office.
- Wi-Fi which is also known as wireless LAN.
(ii) Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
In MAN, computer network can spread across an entire city, college campus, or a small region. It can cover the area of several miles and may include multiple small networks or LANs.
Purpose:
- MANs offer very fast communication but they are expensive to establish. Therefore, only large business organization or universities set up MAN.
- It also requires security measures to prevent unauthorized access.
Some examples of MAN are:
- Cable TV network
- Telephone networks providing high speed DSL lines.
- IEEE 802. 16 or WiMAX, that provides high-speed broadband access with Internet connectivity to customer premises.
(iii) Wide Area Network (WAN):
A Wide Area Network is used for long distance transmission of data. WAN helps to cover a larger geographical area and connect cities, provinces or even countries.
Purpose:
- Using WAN technology, computers may be linked together in different countries using satellites, microwaves or telecommunication links. Therefore, large business, research and educational organizations situated at longer distances use WAN.
- A WAN may include multiple MANs and LANS. WANs are set up with expensive devices and need some dedicated connections.
- Internet is the example of WAN.
Q.No.15: Define Topology. Explain its type?
Ans: Definition Of Topology:
The physical layout in which computers are connected is called topology. The topology of network describes the way computers are connected. Topology is a major design consideration for computer networking.
Types Of Topology:
(i) BUS TOPOLOGY:
- In Bus Topology computers and other devices are connected with a single cable.
- The central cable is the backbone of the network and every device communicates with the other device through this bus.
- It transmits data only in one direction.
The advantages of Bus Topology are:
- Simplicity
- Cable required is least compared to other network topology.
- Used in small networks.
- It is cost effective i.e. low cost
- It is easy to understand.
- Easy expansion of the network i.e. easy to expand joining two cables together
Disadvantage Or Demerit of Bus Topology:
The disadvantage of the Bus Topology is that:
- A breakdown in the bus cable brings the entire network down.
- If network traffic is heavy or nodes are more the performance of the network decreases.
- Cable has a limited length.
- It is slower than the ring topology.
(ii) RING TOPOLOGY:
In Ring Topology, computers are connected in a ring or circle shape. The signal travels around the loop in one direction and passes through each computer.
The recipient of the message receives the message while another computer acts like a repeater to send it to the next computer.
Advantage Or Merit of Ring Topology:
- Transmitting network is not affected by high traffic or by adding more nodes, as only the nodes having tokens can transmit data.
- Cheap to install and expand.
- The failure of a link or a computer can make the entire network nonfunctional.
- Troubleshooting is difficult in ring topology.
- Adding or deleting the computers disturbs the network activity.
(iii) STAR TOPOLOGY:
In a star topology, all the computers are connected to a central device called hub or switch. To communicate with any computer, the sender must send information to the hub. Then the hub transmits that information to the destination.
Advantage Or Merit of Star Topology:
- The advantages of star topology are easy to set up and easy expansion of the network.
- Another feature of Star Topology is that if one link to the hub breaks, only the station using that link is affected not the whole network.
- Fast performance with few nodes and low network traffic.
- Hub can be upgraded easily.
- Easy to troubleshoot.
Disadvantages Or Demerits of Star Topology:
- Cost of installation is high.
- Expensive to use.
- If the hub fails then the whole network is stopped because all the nodes depend on the hub.
- Performance is based on the hub that is it depends on its capacity
Q.No.16: Define standards and network standards. Explain the purpose of standard organisation?
Ans: STANDARDS:
Standards are rules that define the appearance, functionality, or protocols of some equipment.
NETWORK STANDARD:
Network standards define rules of communications among computing devices. This ensures that companies (i.e. Cisco and IBM) that manufacture computing and networking products follow these uniform standards. By following standards, all hardware become compatible in the network, allowing efficient networking to take place. They are essential for network communication.
STANDARD ORGANIZATIONS (PURPOSE):
- Standard Organization develops, coordinates, revises, amends and reissues technical standards.
- These standards are intended to address the requirements of a group of concerned devices.
- There are several organizations working on standardization of computing equipment to enable the interoperability among different devices manufactured by different companies in different regions.
- Example: ISO, IEEE, IETF, ITU and ANSI are the examples of standard organizations.
Q.No.17: Write few lines about different standard organisations?
Ans: (i) International Organization for Standardization (ISO):
- It covers a wide range of fields.
- The ISO has members from the standards committees of various governments across the world.
- It is even responsible for developing models which provides high level of system compatibility, quality enhancement, improved productivity and reduction in costs.
- The ISO is also responsible for endorsing and coordinating the functions of the other standards organizations.
(ii) Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (IEEE):
- It is an international professional non-prot organization.
- Electronics, computer and communication engineers, researchers, scientists and students are the members of IEEE.
- This organization develops communication and information processing standards for all elds related to electrical and computer engineering.
(iii) International Engineering Task Force (IETF):
- It is a large international community of network designers, operators, vendors and researchers concerned with the development of internet architecture and smooth operation of the internet.
(iv) International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- This organization is a specialized agency that is responsible for resolving the issues that concern with information and communication technologies.
(v) American National Standards Institute (ANSI):
- It is the official standards agency for the United States.
- ANSI is a completely private, non-prot organization comprised of equipment manufacturers and users of data processing equipment and services.
- It supervises standards for products, services, processes, systems and personnel in the United States.
- ANSI membership is comprised of people from professional societies, industry associations, governmental and regulatory bodies, and consumer goods.
Q.No.18: Define network architecture?
Ans: NETWORK ARCHITECTURE:
It is the design of a computer network. It is a framework for the specification of a network's physical components, their functional organization and configuration, operational procedures and communication protocols used.
Example: Like OSI / TCP layered architecture.
Q.No.19: Define ISO's OSI model. Name the all layers of OSI's ISO model and describe their functions?
Ans: ISO's OSI Model:
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual model developed by ISO. It characterizes and standardizes the communication functions of a telecommunication and computing network.
Purpose: Its goal is the interoperability of different communication systems with standard 86 communication protocols.
LAYERS OF ISO's OSI MODEL WITH THEIR FUNCTIONS:
This model divides a communication system into seven abstraction layers.
| S.NO. | Layers | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Application |
|
| 2. | Presentation |
|
| 3. | Session |
|
| 4. | Transport |
|
| 5. | Network |
|
| 6. | Data link |
|
| 7. | Physical |
|
Q.No.19: Define TCP/IP model. Name all the layers of TCP/IP model and describe their functions?
Ans: TCP/IP Model:
TCP/ IP is a suite of communication protocols used to interconnect network devices on the internet. These are set of rules and procedures. TCP/IP specifies how data is exchanged over the internet by providing end-to-end communications. It also identifies how data should be broken into packets, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination.
TCP/IP LAYERS WITH THEIR FUNCTIONS:
With reference to OSI layers, we can understand the functions of TCP/IP layers.
| OSI Layers | TCP/IP Layers | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Application Layer |
|
| Presentation | ||
| Session | ||
| Transport | Transport Layer | Using protocols like UDP and TCP, this layer establishes a logical connection between two devices and makes sure the reliable delivery of data. |
| Network | Internet Layer | It is responsible for packet forwarding by accessing physical path. |
| Data link | Network Access Layer | Using the logical addressing this layer decides how data will be sent across different networks paths. |
| Physical |
Q.No.20: What is a network address? OR Define network address?
Ans: NETWORK ADDRESSING:
Network addresses are like our house addresses. They must be unique and distinctive. This avoids confusion for the postman. A network address is any Logical or Physical Address that uniquely identifies it from others. This address is needed to distinguish a network node or device on a computer network. It is a numeric or symbolic number or address that is assigned to any device that seeks access to network or is the part of a network. Physical and Logical Address are different.
Q.No.21: Write down differences between Physical address and Logical address?
Ans: Differences Between Physical Address And Logical address
| S.No. | Physical Address | Logical address |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Physical address is attached with ROM of the NIC card. | Logical address is assigned to a device. |
| 2. | Physical Addressing means MAC (Media Access Control) provided by manufacture and attached address of the NIC. The card which is used to connect your machine to the internet. | Logical addressing means IP addressing that is provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) or set by network administrator. |
| 3. | Physical addressing cannot be can be changed. They are also called hardware address. | Logical Address can be changed. |
| 4. | Physical address is a 48 bit mac address. | Logical address is a 32 bit IP Address. |
| 5. | It is globally Unique and permanent. | It is unique in one network and temporary. |
Q.No.22: Define and explain IPV4 address.
Ans: IPV4 ADDRESS:
- IPV4 stands for Internet Protocol version 4. IP address is a unique number or address used to identify a device on a network. The device could be a computer, printer, smart phone, tablet, etc.
- Every device connected to the internet must have an IP address to communicate with other devices.
- IP address acts as a telephone number or a car registration number.
- It shows ownership and location.
- IP address allows a device to communicate and be located by other devices on the internet.
- IP version 4 (IPV4) addresses are comprised of four number segments separated by dots.
Parts Of IPV4:
An IPV4 address is made up of 32 binary bits, which is divided into two parts:
Network: The network portion of the address mentions the computer network.
Host: The host portion identifies the computer or any other computing device.

























Comments
Post a Comment
If you have any doubts, Please let me know .